Raimona National Park

1. Location and Area of Raimona National Park
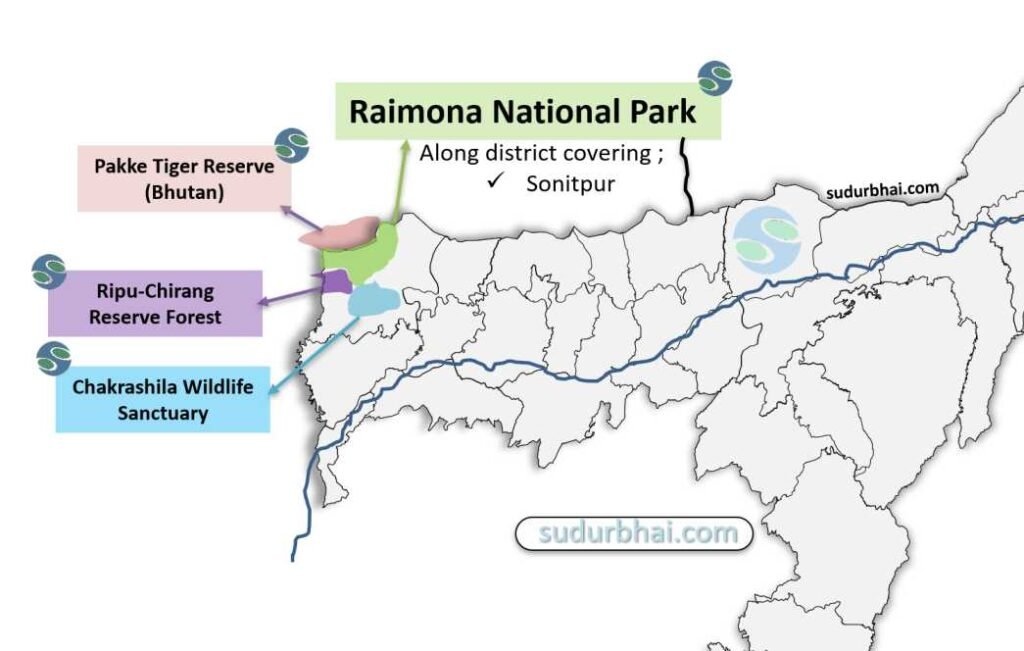
District: Kokrajhar, Assam
Total Area: 422 sq. km
Bordering Regions:
North : Bhutan’s Phibsoo Wildlife Sanctuary
East : Manas National Park’s Buffer Zone.
South : Chakrashila Wildlife Sanctuary.
West : Ripu-Chirang Reserve Forest .
2. Year of Establishment of Raimona National Park
Declared a National Park on June 5, 2021, marking World Environment Day.
Previously part of the Ripu-Chirang Reserved Forest within the Manas Biosphere Reserve.
3. UNESCO and Other Recognitions for Raimona National Park
Though not yet designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, it is a vital extension of the Manas Tiger Reserve, which is a UNESCO-listed site.
Recognized as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) by BirdLife International.
4. Biodiversity of Raimona National Park
Flora of Raimona National Park
Raimona National Park is part of the Eastern Himalayan biodiversity hotspot and features:
Subtropical Moist Deciduous Forests
Semi-evergreen Forests
Bamboo Groves and Grasslands
Dominant Plant Species:
Sal (Shorea robusta)
Teak (Tectona grandis)
Gamari (Gmelina arborea)
Various species of orchids and medicinal plants
Fauna of Raimona National Park
Category | Key Species Found |
|---|---|
Mammals | Golden Langur, Bengal Tiger, Indian Elephant, Indian Gaur, Clouded Leopard, Wild Boar, Leopard Cat |
Birds | Rufous-necked Hornbill, White-winged Duck, Wreathed Hornbill, Great Hornbill, Himalayan Griffon |
Reptiles | King Cobra, Indian Rock Python, Monitor Lizard |
Amphibians | Tree Frogs, Toads, Salamanders |
Insects | Rare species of butterflies and beetles |
5. Major Rivers and Terrain of Raimona National Park
Main Rivers: Saralbhanga, Sankosh, and Ripu, which provide essential water sources for the wildlife.
Landscape Features: Rolling grasslands, dense forests, riverine habitats, and wetland ecosystems.
6. Conservation Challenges and Successes of Raimona National Park
Challenges
Human-Wildlife Conflict: Elephant movement often leads to crop damage in nearby villages.
Illegal Poaching and Encroachment: Threats to rare species such as the Golden Langur and Bengal Tiger.
Deforestation and Habitat Loss: Unregulated extraction of forest resources.
Successes
Inclusion in Manas Tiger Reserve: Ensuring better protection under Project Tiger.
Community-Based Conservation: Engagement of local Bodo tribes in eco-tourism and conservation efforts.
Anti-Poaching Measures: Enhanced patrolling and stricter wildlife protection enforcement.
7. Eco-Tourism and Significance of Raimona National Park
Tourism Potential: Offers adventure trekking, birdwatching, and eco-campsites.
Cultural Importance: Home to indigenous Bodo tribes with a rich cultural heritage.
Connectivity: Well-connected to Kokrajhar town and nearby wildlife reserves.
