Nalbari District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Nalbari District
3. Geography of Nalbari District
4. Socio-Economy of Nalbari District
5. Transport in Nalbari District
6. Demographics of Nalbari District
7. Administrative Setup of Nalbari District
8. Tourist Places in Nalbari District
9. Languages Spoken in Nalbari District
Overview of Nalbari District
- Location: Central Assam, India.
- Established: August 14, 1985, after being carved out from Kamrup district.
- Significance: Known for agricultural richness and cultural diversity, Nalbari is a key player in the socio-economic development of Assam.
History of Nalbari
Early History and Etymology:
- The name “Nalbari” originates from “Nal” (a variety of reed) and “Bari” (enclosed ground with plantation).
- Historically part of Kamarupa, within the Kamapitha division.
- Known as Khata Pargana during Ahom and Mughal rule.
- Archaeological significance: Copper plate inscriptions of Kamrupi kings found in Guwakuchi village.
Bhutan and British India:
- Until the late 19th century, Nalbari was the southern boundary of the Kingdom of Bhutan.
- Duar War: Nalbari was ceded to British India.
- 1833: British divided the valley into Goalpara, Kamrup (including Nalbari), Darrang, and Nagaon.
More Recent History:
- 1890-91: Named “Nalbari” by British Railway Engineers; previously called Satra, Govindapur, and Khata.
- 1920s: Establishment of a railway station led to increased migration and business growth.
- 1967: Declared a subdivision of undivided Kamrup District.
- 1984: Became the district headquarters of Nalbari District.
- April 11, 1986: District and Sessions Judge Court inaugurated.
- Known as the “Navadivipa of Assam” due to its many Sanskrit Toals.
- Famous for Ras Mahotsav, celebrated since the early 20th century.
Geography of Nalbari District
- Area: Approximately 1,052 square kilometers.
- Coordinates: Between 26° N and 26.51° N latitude and 91° E and 91.47° E longitude.
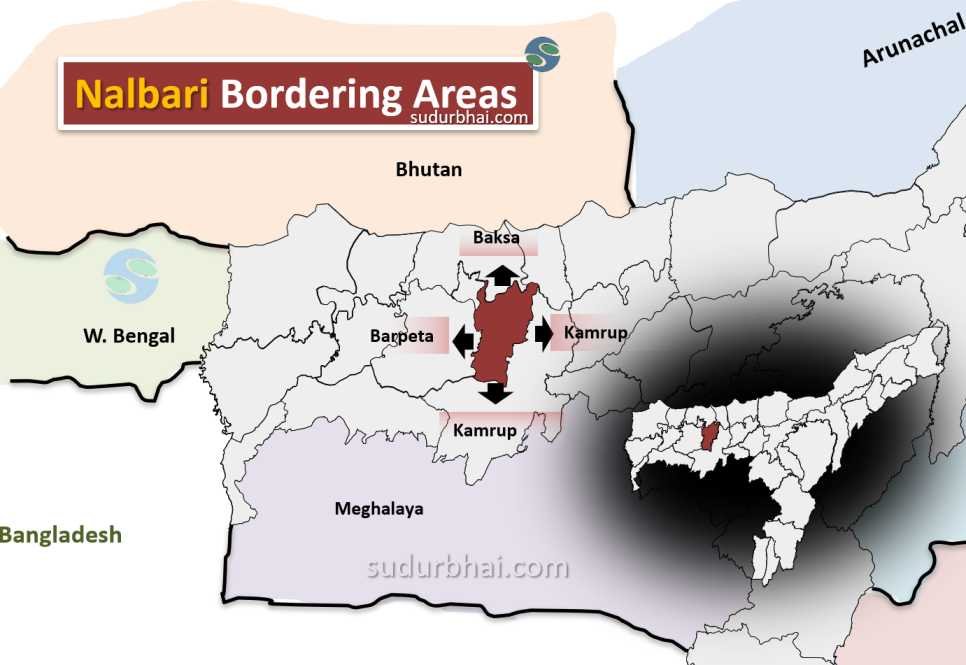
- Boundaries:
- North: Borders Baksa district.
- South: Bordered by Brahmaputra River and Kamrup district.
- East: Adjacent to Kamrup district.
- West: Bordered by Barpeta district.
- Topography: The district has flat terrain with gentle slopes towards the south. It includes low-lying areas that are prone to flooding during the monsoon.
- Climate: Sub-tropical climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Average Annual Rainfall: Around 1,500 mm to 2,000 mm (June to September).
- Impact: Heavy rainfall can cause flooding in low-lying areas .
- Rivers: Major rivers include Buradia, Pagaldia, Nona, Borolia, and Tihu.

Socio-Economy of Nalbari District
- Agriculture: The district’s economy is heavily agrarian. Rice, jute, mustard, potatoes, and vegetables are the main crops.
- Livestock Farming: Cattle, goats, and poultry are important for local livelihoods.
- Small-scale Industries: The industrial sector is underdeveloped, with small industries focused on food processing and bamboo crafts.
- Economic Challenges: Nalbari faces challenges like low per capita income and a high rural population living below the poverty line. Ongoing efforts aim to improve the region’s socio-economic infrastructure.
Transport in Nalbari District
- Roadways: The district is well-connected by roads, including National Highway 31, facilitating travel.
- Railways: The nearest railway station is at Nalbari town, linking the district to other regions in Assam.
- Airways: The nearest airport is in Guwahati, about 70 km away, providing access to major cities.
Demography of Nalbari District
Population Overview
Total Population (2011): 771,639
Males: 396,006 (51.4%)
Females: 375,633 (48.6%)
Gender Distribution
Sex Ratio: 949 females per 1,000 males
Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years): 967 females per 1,000 males
Urban and Rural Population
Rural Population: 688,909 (89.28%)
Urban Population: 82,730 (10.72%)
Age Distribution
Population Aged 0-6 Years: 95,333 (12.35%)
Males: 48,458 (50.9%)
Females: 46,875 (49.1%)
Literacy Rates
Overall Literacy Rate: 78.63%
Male Literacy Rate: 84.36%
Female Literacy Rate: 72.57%
Total Literates: 531,771
Male Literates: 293,184
Female Literates: 238,587
Scheduled Castes and Tribes
Scheduled Castes Population: 60,216 (7.8%)
Scheduled Tribes Population: 23,364 (3.0%)
Population Growth
Population Growth from 2001 to 2011: +11.99%
Density and Area
Area of Nalbari District: 1,052 km²
Population Density: Approximately 733 persons per km²
Administrative Setup of Nalbari District
- District Headquarters: Nalbari town.
- Sub-Divisions: The district has four sub-divisions – Nalbari Sadar, Barama, Barkhetri, and Tamulpur.
- Revenue Circles: Seven revenue circles, including Nalbari, Barkhetri, and Barama.
- Development Blocks: The district has seven development blocks aimed at local governance.
Attractive Tourist Places in Nalbari
- Bamuni Hills: Known for ancient archaeological sites and temple ruins from the medieval period.
- Kamalabari Satra: A prominent Vaishnavite monastery with significant cultural and religious importance.
- Nalbari College: Established in 1950, it has contributed greatly to the region’s educational development.
- Temples and Cultural Sites: The district boasts several temples and cultural sites showcasing Assamese traditions and festivals.
- Billeshwar Temple:
- Over 500 years old, this temple is dedicated to Lord Krishna and attracts numerous Hindu pilgrims.
- Hari Mandir:
- A major landmark associated with the Raas Mahotsav, established in 1965. It is a hub for devotees during the festive season.
- Shripur Devalaya:
- An ancient temple believed to have been constructed by Ahom King Sib Singha, dedicated to Goddess Parvati.
- Basudeb Devalaya:
- Constructed between 1718 and 1744 AD, this temple has a fascinating legend involving Lord Basudeb.
- Daulashal Temple:
- Located in the village of Daulashal, this temple is dedicated to Lord Krishna and Lord Balram.
- Fenguwa Rampart:
- A historical fort built between 1350 and 1365, notable for its length and significance in protecting the kingdom.
- Jaypal Than:
- This temple has folklore associated with its discovery during the reign of King Sib Singha.
- Sonkuriha Bird Sanctuary:
- A prime location for birdwatching, especially during winter when migratory birds flock to the area.
- Buddhist Temple:
- Situated about 30 km from Nalbari town, this temple was established by Nepali settlers in 1965.
- Mahamara Pukhuri:
- An ancient lake constructed by the Ahoms, popular among picnickers.
- Thetha Gohain:
- A serene shrine built at the end of the 19th century, ideal for those seeking tranquility.
- Kakaya Village:
- Known for its thriving cottage industry where visitors can purchase handloom sarees and traditional Assamese textiles.
Languages Spoken in Nalbari District
- Assamese: 85.87% (Nalbari Dialect)
- Bengali: 11.00%
- Bodo: 2.53%
- Others: 0.61%
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
