Nagaon District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Nagaon District
3. Geography of Nagaon District
4. Socio-Economy of Nagaon District
5. Transport in Nagaon District
6. Demographics of Nagaon District
7. Administrative Setup of Nagaon District
8. Tourist Places in Nagaon District
9. Languages Spoken in Nagaon District
District Overview of Nagaon District
- Location: Central Assam, India.
- Significance: Known for agricultural richness, cultural diversity, and historical importance. Nagaon plays a key role in the socio-economic landscape of Assam.
- Administrative Headquarters: Nagaon town.

History of Nagaon District
Early History:
The name “Nagaon” derives from “Na” (new) + “Gaon” (village) → meaning “New Village.”
Eastern, western, and southern fringes were ruled by small feudal kings or their agents.
Under Burmese Rule:
Nagaon remained under Burmese rule until 1826.
British Rule:
Came under British control after the Treaty of Yandaboo (1826).
Nagaon was established as a separate administrative district in 1832 (or 1833, as per another source).
1839: Present-day Nagaon town, initially called Khagorijan, was settled as district HQ, later renamed Nowgong.
1893: Became a municipality.
Recent History:
Judicial activity began in 1967 with the formation of the District Judge Court.
August 15, 2016: Three tehsils were separated to form the Hojai district.
Geography of Nagaon District
- Area: Covers about 2,287 square kilometers.
- Coordinates: Between 25°45′ N to 26°45′ N latitude and 91°50′ E to 93°20′ E longitude.
- Boundaries:
- North: Sonitpur , Bishwanath district.
- South: West Karbi Anglong.
- East: Hojai, Karbi Anglong districts.
- West: Morigaon district.
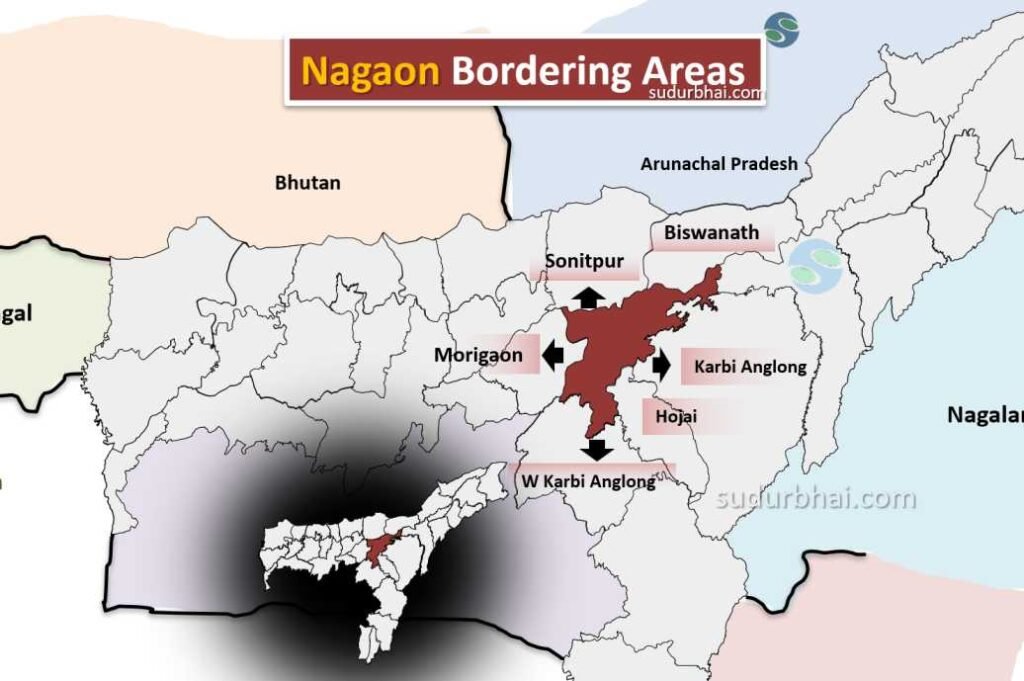
Nagaon Neighbouring districts - Topography: Mostly fertile alluvial plains with some hilly areas. The district has numerous rivers and wetlands.
- Climate: Humid subtropical climate with an average annual rainfall of about 1,500 mm, mostly between June to September.
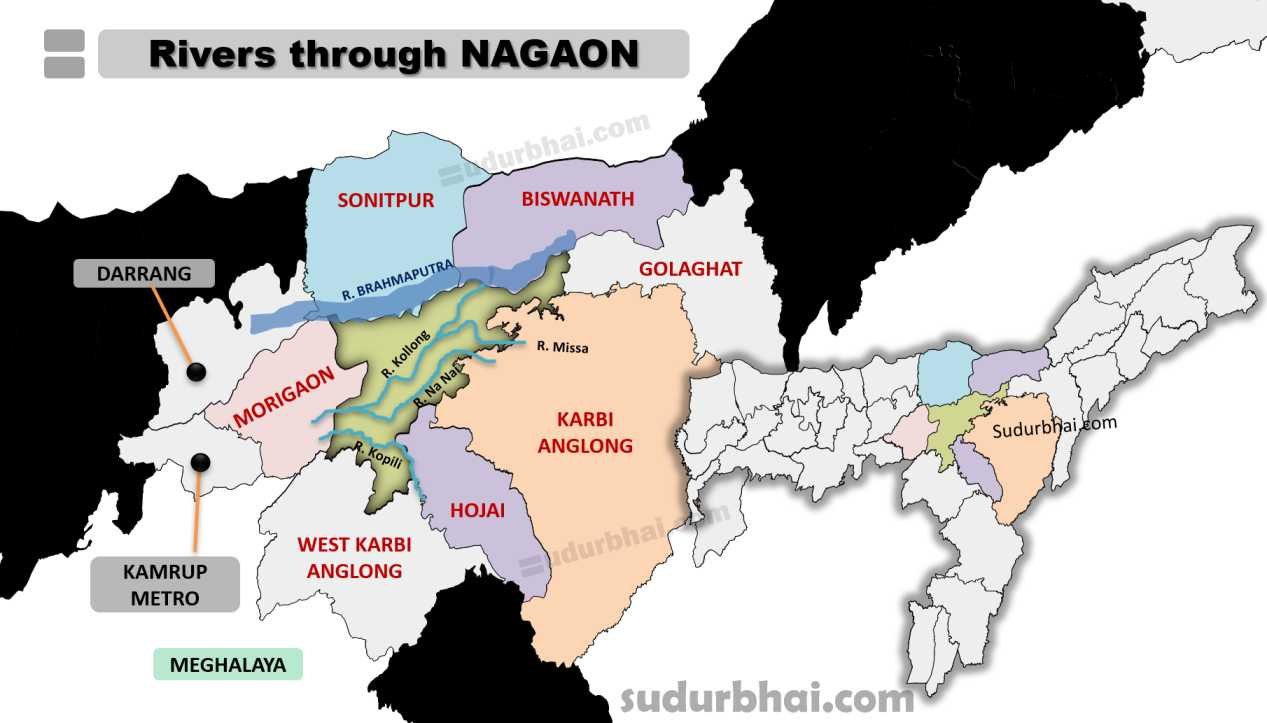
- Rivers: Brahmputra (Northern Border), Kopili, Kollong, Missa, and Na Nai.
Socio-Economy of Nagaon District
- Agriculture: The district’s economy is largely agrarian. Major crops include rice, jute, mustard, potatoes, and various vegetables.
- Livestock Farming: Cattle, goats, and poultry farming play an important role in the economy.
- Small-scale Industries: Includes industries focused on food processing, jute manufacturing, and bamboo crafts.
- Trade and Commerce: Nagaon is a trade hub for agricultural products and handicrafts, with a strong presence of jute mills.
Transport in Nagaon District
- Roadways: Well-connected with roads, including National Highways 36 and 37, making travel easy within the state.
- Railways: Nearest railway stations are in Chaparmukh and Lumding, providing connections to other regions.
- Airways: The nearest airport is in Guwahati, about 120 km away, linking Nagaon to major Indian cities.
Demographics of Nagaon District
Population Overview
Total Population: 2,823,768
Males: 1,439,112 (50.94%)
Females: 1,384,656 (49.06%)
Sex Ratio: 962 females per 1000 males
Child Population (0-6 years): 459,940 (16.29% of total population)
Male Children: 234,203
Female Children: 225,737
Child Sex Ratio: 964 girls per 1000 boys
Rural and Urban Distribution
Rural Population: 2,454,234 (86.91%)
Males: 1,250,985
Females: 1,203,249
Urban Population: 369,534 (13.09%)
Males: 188,127
Females: 181,407
Literacy Rates
Overall Literacy Rate: 72.37%
Male Literacy Rate: 76.51%
Female Literacy Rate: 68.07%
Urban Literacy Rate:
Average: 87.23%
Male: 90.58%
Female: 83.76%
Rural Literacy Rate:
Average: 69.96%
Male: 74.22%
Female: 65.52%
Caste Composition
Scheduled Castes (SC): Constitute approximately 9.4% of the population.
Scheduled Tribes (ST): Constitute about 4.1% of the population.
Administrative Setup of Nagaon District
- District Headquarters: Nagaon town.
- Sub-Divisions: The district has three sub-divisions – Nagaon Sadar, Kaliabor, and Raha.
- Revenue Circles: Seven revenue circles in the district.
- Development Blocks: Thirteen blocks for local governance and development.
Attractive Tourist Places in Nagaon
- Kaziranga National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage site, home to the Indian one-horned rhinoceros.
- Lowkhowa Wildlife Sanctuary: A protected area with diverse flora and fauna.
- Champawati Kunda Waterfall: A scenic waterfall near Chapanala.
- Temples: Including Bratadowa Than (Baishanvi Temple), showcasing Assamese traditions.
- Historical Sites: Relating to the Ahom dynasty and local folklore.
- Samaguri Beel: An ox-bow shaped wetland and lake, also known as Pokhi Tirtha (bird pilgrimage). It is a haven for migratory birds, especially during the winter months.
- Samaguri Satra: A religious and cultural center preserving the tradition of mask-making and local artworks.
- Laokhowa Wildlife Sanctuary: Home to the great Indian one-horned rhino, leopard, tiger, hog deer, and wild cat.
- Silghat: Known for its ancient temples and a river port along the Brahmaputra River. The Trishuldhari Silghat Temple offers a panoramic view of the Brahmaputra.
- Jungal Balahu Garh: This site features a statue of the Tiwa king and brave warrior, Jungal Balahu, and a departmental fishery.
- Hodhodi: A natural waterfall in Lung Chung, approximately 35 km from Nagaon, surrounded by tea gardens and hills
Languages Spoken in Nagaon District
- Assamese: 77.17%
- Bengali: 16.75%
- Hindi: 1.31%
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
