Golaghat District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Golaghat District
3. Geography of Golaghat District
4. Socio-Economy of Golaghat District
5. Transport in Golaghat District
6. Demographics of Golaghat District
7. Administrative Setup of Golaghat District
8. Tourist Places in Golaghat District
9. Languages Spoken in Golaghat District
District Overview of Golaghat District
- Location: Upper Assam, India.
- Established: August 15, 1987.
- Significance: Known for its rich cultural heritage, agriculture, and historical importance. It’s an important administrative and economic hub.
History of Golaghat District
1. Early History
Ahom Rule (16th Century):
Part of Doyang-Dhansiri Valley, ruled by the Ahoms.
Ahom King Suhungmung appointed a Marangi-Khowa Gohain to govern the region.
Encouraged settlements to maintain control and prevent rebellion.
British Annexation (1839–1846):
British East India Company took control of Assam.
1839: Region annexed by the British.
1846: Golaghat became a subdivision of Sibsagar district.
2. Development Under British Rule
Improved Communication & Infrastructure:
1869: Telegraph lines established.
One of Assam’s oldest railway lines built, boosting trade and travel.
Administrative Changes:
After annexation, Assam was divided into Lakhimpur & Sibsagar districts.
Golaghat remained a subdivision under Sibsagar.
3. Post-Independence Era
Formation of Golaghat District (1987):
Became a separate district on August 15, 1987, carved out from Sibsagar.
Cultural Contributions:
Played a role in India’s independence movement (Notable freedom fighters: Kushal Konwar & Kamala Miri).
Literary impact: Hem Chandra Barua wrote the first Assamese dictionary.
Sports: Produced several national athletes.
Geography of Golaghat District
- Area: 3,502 square kilometers (1,352 square miles).
- Boundaries:
- North: Biswanath and Lakhimpur district.
- South: Nagaland.
- East: Jorhat district.
- West: Karbi Anglong and Nagaon districts.
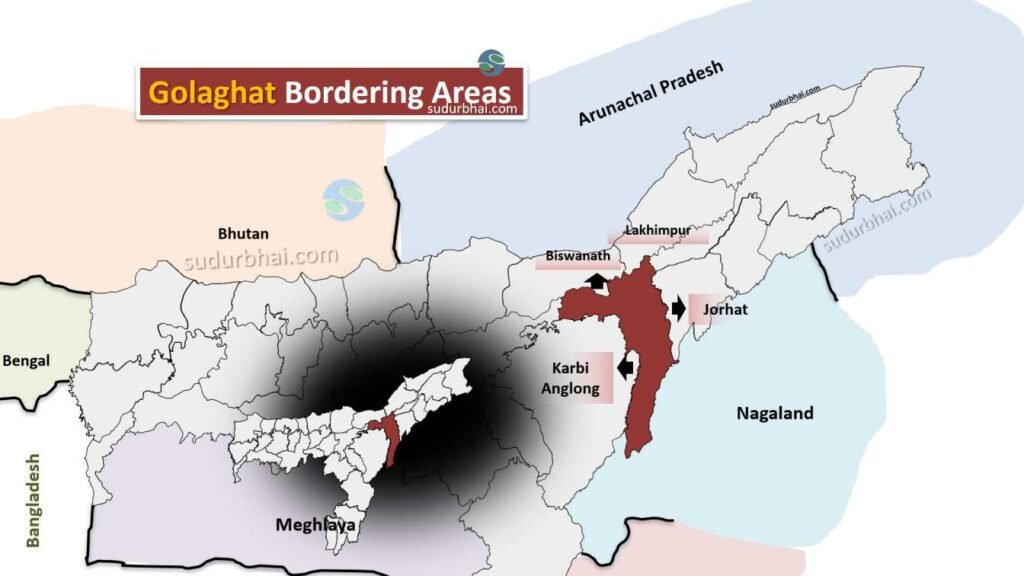
Golaghat neighbouring districts
- Topography: Mostly flat plains with some hilly areas. Fertile soil supports agriculture.
- Rivers flowing through Golaghat – Brahmaputra (making Northern borders), Dhansiri , Diphalu ,Rengma etc.
- Climate: Humid subtropical climate with annual rainfall ranging from 2,012 mm to 2,249.50 mm. Most rainfall occurs during the monsoon (June to September).
Geography of Golaghat District
- Area: 3,502 square kilometers (1,352 square miles).
- Coordinates: 26.52° N latitude and 93.97° E longitude.
- Boundaries:
- North: The Brahmaputra River.
- South: Nagaland.
- East: Jorhat district.
- West: Karbi Anglong and Nagaon districts.
- Topography: Mostly flat plains with some hilly areas. Fertile soil supports agriculture.
- Rivers flowing through Golaghat – Brahmaputra (making Northern borders), Dhansiri , Diphalu ,Rengma etc.
- Climate: Humid subtropical climate with annual rainfall ranging from 2,012 mm to 2,249.50 mm. Most rainfall occurs during the monsoon (June to September).
Socio Economy of Golaghat District
- Economy: Primarily agrarian, with about 80% of the population engaged in agriculture.
- Major Crops: Rtea, rice, and sugarcane.
- Livestock: Includes cattle, goats, and poultry.
- Small-scale Industries: Cottage industries such as Muga silk reeling, Japi making (traditional headgear), and extraction of Agarwood oil.
Numaligarh Oil Refinery is the only major heavy industry in the district, contributing to industrial employment.
Transport of Golaghat District
- Roadways: Well-connected by National Highway 37.
- Railways: The Golaghat Railway Station connects it to other parts of Assam.
- Airways: The nearest airport is in Jorhat, about 56 km away.
Demographics of Golaghat District
Population Overview
Total Population: 1,066,888
Males: 543,161
Females: 523,727
Average Sex Ratio: 964 females for every 1000 males
- Population density : 305 persons per sq km.
Urban and Rural Distribution
Urban Population: 97,736 (9.16% of total)
Male Urban Population: 50,036
Female Urban Population: 47,700
Urban Sex Ratio: 953
Rural Population: 969,152 (90.84% of total)
Male Rural Population: 493,125
Female Rural Population: 476,027
Rural Sex Ratio: 965
Literacy Rates
Overall Literacy Rate: 77.43%
Male Literacy Rate: 83.56%
Female Literacy Rate: 71.09%
Urban Literacy Rate:
Average: 91.74%
Rural Literacy Rate:
Average: 75.94%
Child Population (Age 0-6)
Total Children (0-6 years): 134,793 (12.63% of total population)
Male Children: 68,662
Female Children: 66,131
Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years): 963 girls for every 1000 boys
Ethnic Composition: Primarily Assamese, Bodos, and other indigenous communities.
Administrative Setup of Golaghat District
- Sub-Divisions: Golaghat Sadar, Bokakhat, Dhansiri, and Merapani.
- Revenue Circles: Six circles, including Golaghat, Bokakhat, and Dergaon.
- Development Blocks: Eight blocks, including North Dev Block, Morongi South Block, and Padumani Block.
- Towns: Major towns include Golaghat (Municipal Board), Dergaon, Bokakhat, and Sarupathar.
Attractive Tourist places of Golaghat District
- Kaziranga National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage site, home to the Indian one-horned rhinoceros.
- Sivasagar Sivadol Temple Complex: Historical temples showcasing Assamese architecture.
- Sri Surya Pahar: An archaeological site with remains of Buddhism and Hinduism.
Garampani Hot Springs located in the Nambar Reserve Forest
- Jugibari Beel: A scenic lake and tourist destination
- Negheriting Shiva Doul: An ancient temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, located atop a hill offering views of the Brahmaputra River. The temple is surrounded by tea gardens and is a popular picnic spot
- Uncle Robin’s Children Museum: Showcases personal collections of Dr. Robin, including paintings, dolls, artifacts, and mementos
- Numaligarh Tea Estate: Offers a beautiful location with nearby forests and hills
- Deopahar Ruins: An archaeological site with relics of ancient temples amidst greenery, reflecting the region’s history
- Kakochang Waterfalls: A scenic waterfall near Kaziranga National Park and Bokakhat, surrounded by tea gardens and rubber plantations, ideal for trekking and picnics
- Srimata Sankardev Udyan: A park dedicated to the saint Srimanta Sankardev, offering well-maintained gardens and a serene atmosphere for relaxation
- Doigrung Wildlife Sanctuary: Known for diverse species of plants and animals, including elephants and deer. It is a haven for bird watchers and wildlife photographers
- Birangana Sadhoni Kalakshetra: A cultural center dedicated to preserving and promoting the local culture through dance, music, theatre, and workshops
Languages spoken in Golaghat District
- Assamese: 78.40%
- Bengali: 4.59%
- Mising: 2.71%
- Nepali: 2.50%
- Boro: 1.86%
- Hindi: 1.79%
- Sadri: 1.52%
- Odia: 1.36%
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
