Dibrugarh District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Dibrugarh District
3. Geography of Dibrugarh District
4. Socio-Economy of Dibrugarh District
5. Transport in Dibrugarh District
6. Demographics of Dibrugarh District
7. Administrative Setup of Dibrugarh District
8. Tourist Places in Dibrugarh District
9. Languages Spoken in Dibrugarh District
District Overview of Dibrugarh District
- Location: Northeastern Assam, India.
- Nickname: Often called the “Tea Capital of India” due to its famous tea gardens.
- Key Features: Known for its extensive tea plantations, rich cultural heritage, and historical importance.
History of Dibrugarh District
- Chutia Kingdom (Pre-1523 AD): Originally part of the Chutia Kingdom before being annexed by the Ahoms in 1523.
- Ahom Rule: Ahoms defeated the Chutias at Dibrumukh; King Suhungmung appointed officials to govern the region.
- Moamoria Rebellion (1787-1805): Significant uprising against Ahom rule during King Gaurinath Singha’s reign, shifting power dynamics in the region.
British Colonial Era
- British Arrival (1826): Following the Treaty of Yandaboo, the British recognized Dibrugarh’s administrative and commercial potential.
- Administrative Center (1842): Became headquarters of Lakhimpur District under British rule.
- World War II Role: Functioned as a key military base and transit camp for evacuees from Burma.
Geography of Dibrugarh District
- Area: 3,381 square kilometers.
- Boundaries:
- North: Dhemaji District.
- South: Charaideo and Sibsagar district.
- East: Tinsukia district.
- West: Lakhimpur district.
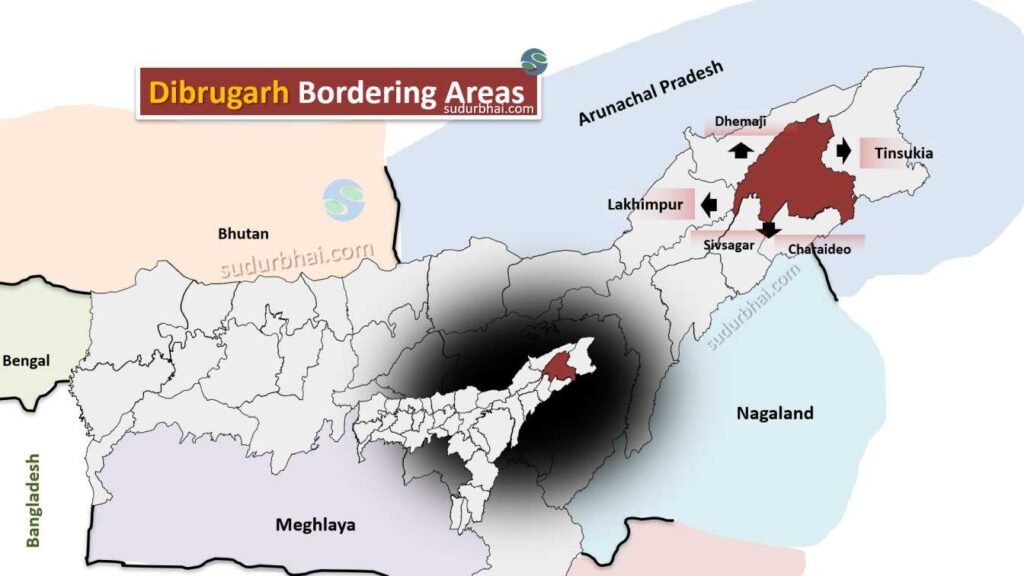
Dibrugarh neighbouring Districts
- Topography: A mix of flat plains and gentle hills, with the Brahmaputra River flowing along the southern boundary.
- Rivers: The Brahmaputra (avg. width here =10 km)and its tributaries (Lohit, Burhidihing) contribute to the district’s fertile soil.
- Climate: Humid subtropical with heavy monsoon rainfall. Temperatures range from 10°C in winter to 39°C in summer. Average annual rainfall is 2,518 mm.
- Avg. annual rainfall decreases from Dibrugarh(North) to Naharkatia (south)
Socio Economy of Dibrugarh District
- Economy: Primarily agrarian, with a major focus on tea. Also known for Oil.
The Assam gas cracker project (a.k.a. Brahmaputra Cracker and Polymer Limited (BCPL)).
Dhuliajan, and important oil town – known for crude oil as well as Natural Gas reserve.
Namrup has countries first fertilizer factory and recently established thermal power plant.
- Tea Industry: Dibrugarh is home to 178 tea gardens, contributing significantly to the economy.
- Other Agriculture: Rice, jute, mustard, and various fruits are also cultivated.
- Small-Scale Industries: Food processing, handicrafts, and bamboo products.
- Tourism: The district’s natural beauty, tea estates, and cultural sites attract many tourists.
Transport in Dibrugarh District
- Roadways: National Highway 15 connects Dibrugarh to other parts of Assam. It also has many state highways and rural roads.
- The Bogibeel rail cum road bridge which is the longest Railway Bridge in the country and 5th Bridge across the river Brahmaputra – connect Dibrugarh and dhemaji (through NH 15)
- Railways: The Dibrugarh Railway Station connects the district to major cities like Guwahati and Kolkata.
- Airways: Dibrugarh Airport (Mohanbari Airport) only.
Demographics of Dibrugarh District
Population Statistics (2011 Census)
Total Population: 1,326,335
Male Population: 676,434 (51.0%)
Female Population: 649,901 (49.0%)
Rural Population: 1,082,605 (81.62%)
Urban Population: 243,730 (18.38%)
Sex Ratio
Overall Sex Ratio: 961 females per 1000 males
Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years): 962 females per 1000 males
Literacy Rate
Average Literacy Rate: 76.05%
Male Literacy Rate: 82.82%
Female Literacy Rate: 68.99%
Languages Spoken
The linguistic demographics of Dibrugarh District are as follows:
Assamese: 76.01%
Bengali: 5.93%
Hindi: 5.80%
Sadri: 4.83%
Nepali: 1.72%
Child Population
Total Child Population (0-6 years): 163,210
Male Children: 83,168
Female Children: 80,042
Child Proportion (0-6 years): Approximately 12.31% of the total population
Administrative Setup Dibrugarh District
- Established: October 2, 1971 (carved out from Lakhimpur district).
- Sub-Divisions: Two sub-divisions – Dibrugarh (Sadar) and Tinsukia.
- Development Blocks: Seven blocks – Khowang, Borboruah, Lahowal, Tengakhat, Joypur, Tinkhong, and Panitola.
- Towns: Major towns include Dibrugarh, Chabua, Naharkatia, and Namrup.
Tourist Places in Dibrugarh District
- Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary This sanctuary is the only rainforest in Assam, with a diverse array of flora and fauna. It is home to over 293 bird species, 47 mammal species, and various reptiles and butterflies.
- Tea Gardens: Explore expansive tea estates with guided tours and tastings.
- Brahmaputra Riverfront: Enjoy beautiful views and leisure activities like boating and picnicking.
- Jeypore Rainforest: A biodiversity hotspot with rich flora and fauna.
- Assam Medical College & Hospital: One of Asia’s oldest medical colleges, located in Dibrugarh town.
- Jokai Botanical Garden cum Germplasm Center This garden features endangered plant species
- Barbarua Maidam This site is a graveyard featuring the graves of high-ranking officials from the Ahom Dynasty.
- Dinjoy Satra This Satra provides insights into Assamese history and culture. It has been relocated several times and is now a significant cultural site in Dibrugarh.
- Shri Jagannath Temple A replica of the Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha, this temple is known for its spiritual environment and distinctive architecture.
- Namphake Village: Visit this village to see a gold-plated statue of Lord Buddha in the main temple
Languages Spoken in Dibrugarh District
- Assamese: 76.01%
- Bengali: 5.93%
- Hindi: 4.79%
- Bhojpuri: 0.42%
- Nepali: 0.12%
- Other languages: 13.73%
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
