Dehing Patkai National Park

1. Location and Area of Dehing Patkai National Park
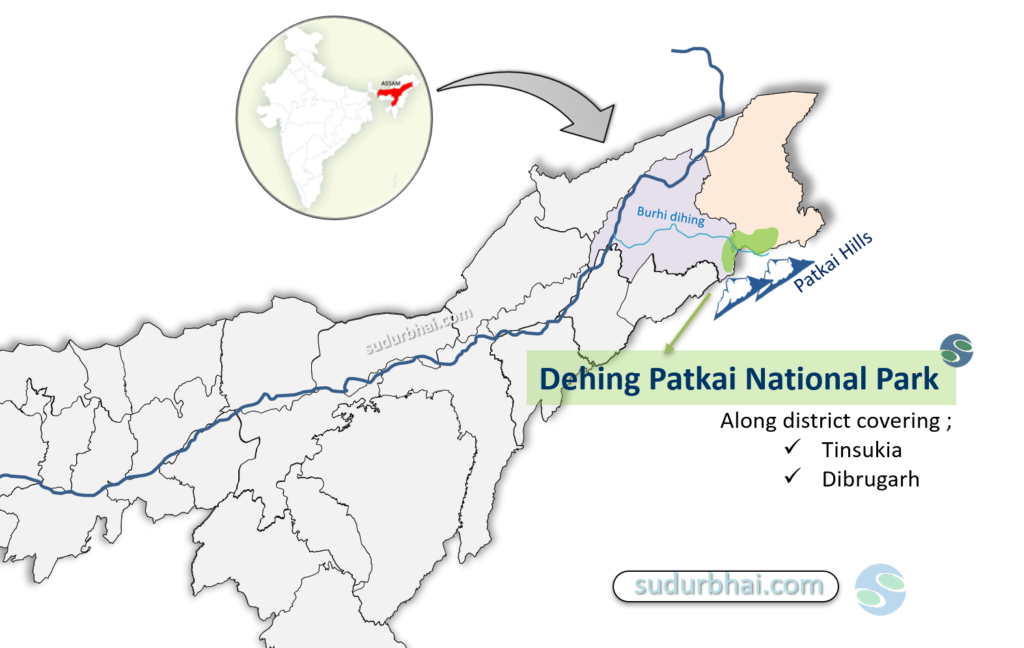
- Geographical Location: Located in eastern Assam, near the foothills of the Patkai Hills along the Assam-Arunachal Pradesh border.
- Districts Covered: Dibrugarh and Tinsukia.
- Total Area: 234.26 sq. km
- Landscape Features:
- Part of the Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot.
- Dense tropical evergreen rainforest, often called the “Amazon of the East”.
- Hilly terrain with rich flora and fauna, multiple rivulets, and high rainfall.
2. Year of Establishment of Dehing Patkai National Park
Declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary: 2004.
Upgraded to National Park: June 2021 (Making it Assam’s 7th National Park).
3. Biodiversity of Dehing Patkai National Park
A. Flora of Dehing Patkai National Park
Vegetation Types:
Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests (Largest stretch of this forest type in Assam).
Semi-evergreen forests.
Moist deciduous patches in the lower regions.
Dominant Plant Species:
Trees: Hollong (State tree of Assam), Mekai, Nahor, Bhelu, and Kaindal.
Orchids: Abundant varieties found in the dense canopy.
Canopy Structure: Multi-layered forests with thick undergrowth, creepers, and ferns.
B. Fauna of Dehing Patkai National Park
Mammals
Key Species:
Asian Elephant (Common in the park, part of the larger Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve).
Leopard, Clouded Leopard (Vulnerable species), Golden Cat.
Hoolock Gibbon (India’s only ape species, vulnerable).
Malayan Giant Squirrel, Porcupine, and Pangolin.
Chinese Pangolin (Critically endangered species).
Avifauna (Birdlife – Important Bird Area by BirdLife International)
More than 300 bird species recorded.
Key Bird Species:
Great Hornbill and Wreathed Hornbill (Flagship species for conservation).
Hill Myna, Green Pigeon, and Sultan Tit.
Migratory Birds: Several species of warblers and flycatchers visit seasonally.
Reptiles & Amphibians
King Cobra, Indian Rock Python, Monitor Lizards, and Tree Frogs.
4. Major Rivers and Terrain of Dehing Patkai National Park
A. Major Rivers of Dehing Patkai National Park
- Dihing or Burhi Dihing Rivers: The park is named after this river, which flows through the region.
B. Terrain & Climate of Dehing Patkai National Park
Landscape:
Hilly and undulating terrain, part of the Patkai Hill Range.
Dense rainforest with rich biodiversity.
Climate:
Humid subtropical climate with heavy rainfall.
Annual Rainfall: 3800-4000 mm (One of the wettest regions of Assam).
Temperatures: Summers (20-35°C), Winters (7-18°C).
5. Conservation Challenges and Successes in Dehing Patkai National Park
A. Conservation Challenges in Dehing Patkai National Park
Coal Mining and Deforestation
Illegal coal mining in the nearby Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve has severely impacted the ecosystem.
“Rat-hole” mining and deforestation threaten the forest cover and wildlife habitat.
Encroachment and Habitat Destruction
Expansion of settlements and agricultural land near the park reduces its buffer zone.
Poaching of pangolins, hornbills, and illegal timber logging are major issues.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Frequent conflicts between elephants and local communities due to habitat fragmentation.
Oil Exploration and Industrial Threats
Oil drilling activities nearby (by ONGC and Coal India Ltd.) raise concerns about pollution.
2020 controversy over proposed coal mining near the sanctuary led to protests and a demand for better conservation measures.
B. Conservation Successes in Dehing Patkai National Park
Upgrade to National Park Status (2021)
Helped improve legal protection and stricter regulations on mining and logging.
Extended area under the protected zone to prevent deforestation.
Better Elephant Conservation Strategies
Part of the larger Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve, ensuring better wildlife corridors for elephants.
Increased Awareness and Protests Against Mining
Public protests and environmental activism helped stop coal mining approvals in 2020-21.
Improved Eco-Tourism and Sustainable Development
More focus on eco-friendly tourism and nature trails to boost conservation-based tourism.
6. Eco-Tourism and Adventure Activities in Dehing Patkai National Park
Jungle Trekking and Nature Walks: Exploring the rainforests, rivulets, and hilly terrain.
Birdwatching Tours: One of Assam’s best birding destinations.
Wildlife Photography Expeditions: Spotting rare mammals, reptiles, and orchids.
Ethnic Tourism: Visiting nearby tribal villages (Singpho, Tai Phake, and Khamti communities).
River Rafting & Angling: Available in Burhi Dihing River.
