Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
3. Geography of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
4. Socio-Economy of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
5. Transport in Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
6. Demographics of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
7. Administrative Setup of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
8. Tourist Places in Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
9. Languages Spoken in Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
District Overview of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
- Location: In the central part of Assam, India.
- Established: February 3, 2003 after the bifurcation of the old Kamrup district.
- Significance: Includes Guwahati city, the administrative headquarters, and is an economic hub with a rich cultural heritage.
History of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
1. Ancient History
The region was once called Pragjyotishpur, meaning “the light of the East”, due to the prominence of astrology and astronomical studies.
The name “Guwahati” originates from Assamese words:
“Guwa” (Areca nut)
“Haat” (Market) → Indicating the region’s historical role as a trading hub.
Ancient texts, including the Mahabharata and other Sanskrit epics, referred to Assam as Kamrup.
According to legend, the demon king Narakasura built the ancient city of Pragjyotishpur.
Another popular legend links the name “Kamrup” to the story of Lord Shiva and Kamadeva (the God of Love), who was turned into ashes but later revived in this region.
2. Medieval History
Kamrup was a strategic region between the Ahom and Koch kingdoms.
Neither the Mughals nor the Koch dynasty could maintain long-term control over Guwahati due to frequent power struggles.
The Ahom rulers appointed a Borphukan (Governor), who held both civil and military authority in Kamrup, with Guwahati as his headquarters.
The region witnessed multiple battles between the Ahoms and the Mughals, culminating in the Battle of Saraighat (1671), where Lachit Borphukan led the Ahoms to victory against the Mughals.
3. Modern History
Guwahati has emerged as a major commercial center and an important transit hub connecting six North Eastern states of India.
1907: The Kamrup Industrial & Trading Company Limited was founded in Guwahati, becoming Assam’s first indigenous joint-stock company. It played a crucial role in the Swadeshi movement, promoting Indian-made goods.
Amingaon, near the historic Battle of Saraighat site, became the headquarters of Kamrup district in 2009 after Kamrup was divided.
The Kamrup (Metro) district has its administrative headquarters in Guwahati, the largest city in Assam.
Geography of Kamrup (Metropolitian) District
- Area: Approximately 955 square kilometers.
- Coordinates: Around 25°43′ N latitude and 91°36′ E longitude.
- Boundaries:
- North: Darrang district.
- South: Meghalaya.
- East: Morigaon district.
- West: Kamrup district.
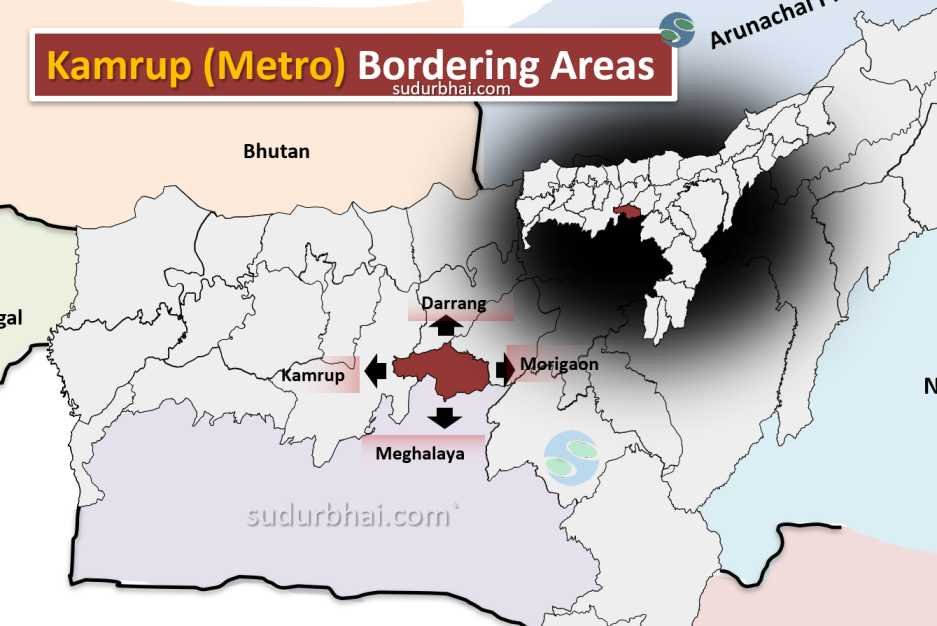
Kamrup metro Neighbouring districts - Topography: A mix of flat plains and hilly terrains. The Brahmaputra River significantly shapes the landscape.
- Climate: Humid subtropical climate with 1,500 mm to 2,600 mm average annual rainfall (mostly in the monsoon season from June to September).
- River : Brahmaputra (Northern Border) , Basistha, Bharalu , Digharu and Kopili

Socio-Economy of Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
- Economy: Diverse and dynamic, with industries, agriculture, and the service sector contributing significantly.
- Major Industries: Tea processing, handloom, handicrafts, and small-scale manufacturing. Guwahati is also home to software technology parks.
- Agriculture: Important crops include rice, jute, mustard, and fruits.
- Service Sector: Thriving due to urbanization, with educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and commercial establishments.
- Tourism: The cultural and natural attractions boost the local economy.
Transport of Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
- Roadways: Well-connected through National Highways 31 and 37, linking it to other parts of Assam.
- Railways: Guwahati Railway Station and Kamakhya Railway Station connect Kamrup (Metro) to other regions.
- Airways: Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport in Guwahati connects the district to major cities across India.
Demographics of Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
Population:
- Total population: 1,253,938
- Male: 647,585
- Female: 606,353
- Sex Ratio: 936 females per 1000 male
- Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years): 946 females per 1000 males
- Children (0-6 years): 10% of the population
- Urban population: 82.7%
- Rural population: 17.3%
Caste:
- Scheduled Caste: 8.1% of the population
- Scheduled Tribe: 6% of the population
Literacy:
- Literacy rate: 88.71%
- Male literacy: 92.13%
- Female literacy: 85.07%
- Urban literacy rate: 91.19%
- Rural literacy rate: 76.45%
Religion:
- Hinduism: 84.89%
- Muslim: 12.05%
Population Density:
- Density: 1,313 people per square kilometer
Administrative Setup of Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
- Sub-Divisions: One sub-division – Guwahati Sadar.
- Revenue Circles: Five circles – Azara, Chandrapur, Dispur, Guwahati, and North Guwahati.
- Development Blocks: Three blocks – Chandrapur, Dimoria, and Rani.
- Municipal Wards: 31 municipal wards in Guwahati city.
Tourist Places in Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
Religious Sites:
- Kamakhya Temple: A sacred site known for its Tantric traditions, located on Nilachal Hill. It’s considered one of the greatest of all the saktipithas in India.
- Hayagriva Madhava Temple: Situated in the Monikut hill of Hajo, believed to have been constructed in 1583 by Raghudeva Narayan. A big pond called Madhava Pukhuri is located near the temple.
- Poa Mecca: A place where the famous seer Giyasuddin Auliya was buried. It is believed that a devotee offering prayer in this dargah gains one-fourth of the spiritual enlightenment which can be gained at Mecca.
- Umananda Temple: Located on an island in the middle of the Brahmaputra River.
- Navagraha Temple: A temple containing nine phallic emblems of Shiva covered with cloths of different colours sacred to the nine planetary gods.
Wildlife and Nature:
- Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary: A wildlife reserve located about 30 km east of Guwahati.
- Assam State Zoo cum Botanical Garden: Features a wide range of animals in replicated natural habitats and a herbarium.
- Deepor Beel: A large natural wetland and a bird sanctuary with a variety of local and migratory birds.
Historical and Cultural Sites:
- Saraighat War Memorial Park: Commemorates the Battle of Saraighat fought between the Ahoms and the Mughals in 1671.
- Assam State Museum: Showcasing the history and culture of Assam.
- Srimanta Sankardeva Kalakshetra: A cultural complex with museums, parks, and theaters.
- Gandhi Mandap: A memorial dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi, located on top of the Sarania Hillock.
Other Attractions:
- Guwahati Planetarium: Offers shows related to astronomy
Languages Spoken in Kamrup (Metropolitan) District
- Assamese (57.87%)
- Bengali (20.50%)
- Hindi (10.45%)
- Nepali (2.39%) and
- Boro (1.66%)
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
