Goalpara District
INDEX
1. District Overview
2. History of Goalpara District
3. Geography of Goalpara District
4. Socio-Economy of Goalpara District
5. Transport in Goalpara District
6. Demographics of Goalpara District
7. Administrative Setup of Goalpara District
8. Tourist Places in Goalpara District
9. Languages Spoken in Goalpara District
Overview of Goalpara District
- Location: Western Assam, India.
- Named After: The word “Gwaltippika,” meaning “the village of milkmen.”
- Cultural Heritage: Known for its diverse culture, archaeology, and agricultural economy.
History of Goalpara District
1. Early History
- Ancient Period (1st Millennium CE): The region was originally part of the Kamarupa Kingdom, an important kingdom in ancient Assam.
- Medieval Period (Late 16th Century): It later became part of the Kamata Kingdom, which ruled over parts of Assam and Bengal. Eventually, it was taken over by Koch Hajo, a kingdom founded by the Koch rulers.
- Ahom-Mughal Wars (1619–1682): The region witnessed intense battles between the Ahoms and the Mughals. After the Ahom victory in 1682, the Mughals lost control, but during their rule, the region was included in the Bengal Subah (province) and was known as Sarkar Dhekuri.
2. Colonial Era
- 1765 – British Annexation: After the British East India Company defeated the Nawabs of Bengal, Goalpara came under British control along with the rest of Bengal.
- 1816 – Special Administrative Unit: The British created a special administrative unit called “North-Eastern Parts of Rangpur”, placing it under the charge of David Scott, who was appointed as the Civil Commissioner.
- 1822 – Formation of Goalpara District: The British officially formed Goalpara District, which included territories from the Bijni Kingdom and parts of the Garo Hills. It became an important administrative region in Northeast India.
3. Administrative Changes
- 1866 – Separation of Garo Hills: The British detached Garo Hills from Goalpara, making it a separate administrative unit. They also formed a new district named Greater Koch Behar.
- 1874 – Merging with Assam Valley Province: Goalpara was merged into the newly created Assam Valley Province, which included most of present-day Assam.
- 1983 – Creation of Present Goalpara District: Over time, Goalpara was divided into four districts:
- Goalpara
- Dhubri
- Kokrajhar
- Bongaigaon
Geography of Goalpara District
- Area: 1,824 square kilometers.
- Boundaries:
- North: Bongaigaon, Borpeta.
- South: Meghalaya (Garo Hills).
- East: Kamrup district.
- West: Dhubri, South-salmara Manchachar district.
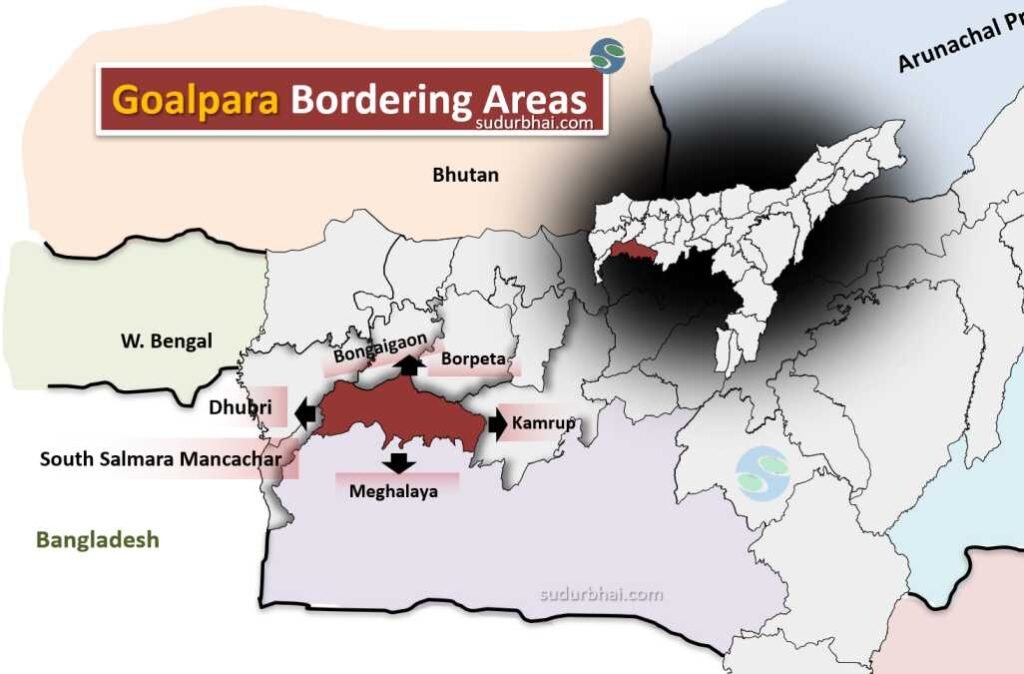
Goalpara bordering districts
- Major physiographic zones:
Zone
Description
Northern Alluvial Plains Fertile land along the Brahmaputra, ideal for agriculture. Southern Hills Part of the Meghalaya Plateau, with rugged terrain and forests. Riverine Floodplains Low-lying areas prone to seasonal flooding. - Beels: Urpad , Nalga, Kumri etc.
- Climate: Humid Subtropical Climate
- Summer (March–June): Hot and humid, temperatures range from 25°C to 35°C.
- Monsoon (June–September): Heavy rainfall due to the Southwest Monsoon, annual precipitation around 2200-2800 mm.
- Winter (November–February): Cool and dry, temperatures range from 10°C to 22°C
- Land Use Pattern in Goalpara:
Category Percentage of Total Land Agricultural Land 55% Forest Cover 20% Water Bodies 10% Others (Urban/Rural Settlements, Grasslands, etc.) 15%
- Land Use Pattern in Goalpara:
- Agriculture in Goalpara :
Category Major Crops Cereals Paddy, Wheat, Maize Oilseeds Mustard, Sesame Pulses Lentils, Gram, Peas Cash Crops Jute Horticultural Crops Areca Nut, Banana, Vegetables - Forests and Vegetation:
- Goalpara has a mix of dense forests and open grasslands, particularly in the southern region.
- Major forest types:
- Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests
- Evergreen and Semi-evergreen Forests in hilly areas
- Important Wildlife Areas:
- Dudhnai Reserve Forest (Rich in biodiversity, home to various flora and fauna).
- Hulukanda Forest (Known for its population of Hoolock Gibbons).
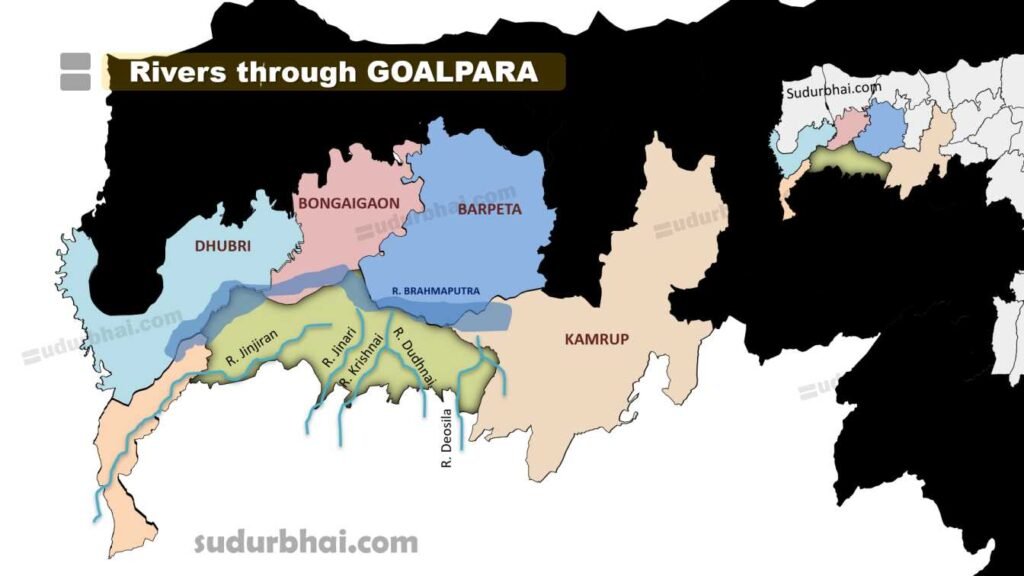
- Rivers : Brahmaputra (northern border), Dhudhnoi , Krishnai, Deosila, Jinjiran.
- Agriculture in Goalpara :
Socio-Economy of Goalpara District
- Economy: Agricultural economy with farming as the main occupation (>90% population )
- Major Crops: Rice, jute, mustard, and various fruits. Jute production is especially important.
- Livestock: Cattle and poultry farming are common.
- Handicrafts & Small Industries: Bamboo and cane products are traditional crafts in the area.
- Tourism: The district has a rich history and several archaeological and natural attractions that boost tourism.
Transport in Goalpara District
- Roadways: The district is well-connected by National Highway 27, linking it to major cities in Assam.
- Naranarayan Setu (third Bridge over the river Brahmaputra) has connected pancharatna of goalpara and Jogi Jhopa of Bongaigaon district
- Railways: Goalpara town has the nearest railway station.
- Airways: The closest airport is in Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport, Guwahati (GAU)
Demographics of Goalpara District
Population
- Total Population: 1,008,183
- Male Population: 513,292 (50.9%)
- Female Population: 494,891 (49.1%)
- Total Population: 1,008,183
Sex Ratio
- Overall Sex Ratio: 964 females per 1000 males
- Child Sex Ratio (0-6 years): 963 girls per 1000 boys
Age Distribution
- Children (0-6 years): 171,657 (17.03% of total population)
- Male Children: 87,457
- Female Children: 84,200
- Children (0-6 years): 171,657 (17.03% of total population)
Literacy Rate
- Overall Literacy Rate: 67.37%
- Male Literacy Rate: 71.46%
- Female Literacy Rate: 63.13%
- Overall Literacy Rate: 67.37%
Urban and Rural Distribution
- Urban Population: 138,062 (13.69%)
- Rural Population: 870,121 (86.31%)
- Population Density : 553 persons per sq. KM
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes
- Scheduled Castes: 4.47% of the population
- Scheduled Tribes: 22.97% of the population
Administrative Setup of Goalpara District
- Created: Officially established in 1983 after being carved out from the old Goalpara district.
- Sub-Divisions: Goalpara Sadar and North Salmara (merged into Bongaigaon district in 1989).
- Revenue Circles: Five – Lakhipur, Baliana, Matia, Dudhnoi, and Rangjuli.
- Development Blocks: Eight blocks, including Rangjuli, Kusdhowa, and Matia.
- Police Stations: Ten police stations for law and order.
Attractive Tourist Places
- Sri Surya Pahar: An archaeological site with relics of Buddhism, Jainism, and Hinduism. A.k.a. the “Ellora of North East“
- Dadan Hill: Home to a Shiva temple, established by a general from King Bana’s army.
- Tukreswaree Hill – People believe that while Mahadev was wondering about the earth with Sati’s body, one of her Limbs fell on the spot, where the temple is situated
- Pir Majhar: A revered tomb in Goalpara town.
- Hulukanad Hill: A scenic hill offering panoramic views.
- Kumri Beel Lake : Located near Narnarayan Setu, this picturesque lake is ideal for bird watching, especially during the migratory season. It offers opportunities for picnicking and boating amidst lush greenery.
- Pir Saheb Majar Shariff : A significant religious site dedicated to the Sufi saint Sayed Nasiruddin Kadri (Bagdadi), attracting many visitors during the annual URS festival.
- Shyamrai Satra : A center of Vaishnavite culture, this place is important for followers of the faith and offers insights into local traditions
Languages Spoken in Goalpara District
- Assamese: 51.78%
- Bengali: 28.83%
- Garo: 7.56%
- Rabha: 5.16%
- Bodo: 3.53%
- Hindi: 0.94%
Let us know any further suggestions ,we at sudurbhai.com will be happy to hear from you in our comment section below !
